The Musculoskeletal System's Response to Acute Exercise
The responses to acute exercise for the musculoskeletal system can be described in many ways. The skeletal system have many responses to acute exercise. It can have an increased Osteoblast activity at the points of stress, there is also an increase of synovial fluid production, this means that more synovial fluid is released into the joints also indicating there is more cushion between the joints. this is good as it prevents them from rubbing together causing friction. Another response to this is that there is an increase in blood supply, this is also good as it allows more movement from the muscles and bones. There is also an increased blood flow to the ligaments and tendons, this allows a greater range of movement and means there is a less likely hood of a tear due to the increased elasticity.
The capillaries dilate to allow more oxygen to be delivered to the working muscles.
This is also good as the muscles need specific nutrients to help them function and work properly. One of these nutrients is oxygen and a more plentiful supply of this helps the muscles work better and faster and last longer. There will also be an increased muscle pliability as a response of acute exercise on the body, muscles warm up during the activity by stretching and running or doing any physical exercise, this means that they are able to change shape and size more easily. This means that they will also be less likely to get strained, pulled or torn as they are fully flexible when they are warmed up and loosened up.
There will also be an increase of joint mobility as a response to the acute exercise, the joints are lubricated which can means they are watered or cushioned to prevent them from rubbing together causing friction, discomfort and pain. this can also mean Viscosity, this is the term used for the loosening up of the joint and equaling more movement. the synovial fluid also helps as it is like a cushion.
Another type of response is that muscle fiber tears, muscles can become under a lot of stress during an exercise, this can then lead to tiny tears appearing in the fibers. This can be due to plyometric eccentric contractions, these cause tears, they can be done by jumping from a height. The tissue then swells and it takes a rest or recovery time for them to repair.
Energy Systems in Sports
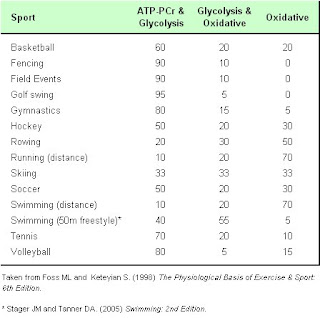
Energy for a 100 meter sprinter is different to other sports, they require 50% from the ATP-PC system and 50% from the anaerobic glycolysis system. Marathon runners are different again from sprinters as they require only the aerobic system.
This table shows how each of the energy system's contribute to to meet the physical demands of the sports.
The capillaries dilate to allow more oxygen to be delivered to the working muscles.
This is also good as the muscles need specific nutrients to help them function and work properly. One of these nutrients is oxygen and a more plentiful supply of this helps the muscles work better and faster and last longer. There will also be an increased muscle pliability as a response of acute exercise on the body, muscles warm up during the activity by stretching and running or doing any physical exercise, this means that they are able to change shape and size more easily. This means that they will also be less likely to get strained, pulled or torn as they are fully flexible when they are warmed up and loosened up.
There will also be an increase of joint mobility as a response to the acute exercise, the joints are lubricated which can means they are watered or cushioned to prevent them from rubbing together causing friction, discomfort and pain. this can also mean Viscosity, this is the term used for the loosening up of the joint and equaling more movement. the synovial fluid also helps as it is like a cushion.
Another type of response is that muscle fiber tears, muscles can become under a lot of stress during an exercise, this can then lead to tiny tears appearing in the fibers. This can be due to plyometric eccentric contractions, these cause tears, they can be done by jumping from a height. The tissue then swells and it takes a rest or recovery time for them to repair.
Energy Systems in Sports
Energy for a 100 meter sprinter is different to other sports, they require 50% from the ATP-PC system and 50% from the anaerobic glycolysis system. Marathon runners are different again from sprinters as they require only the aerobic system.
This table shows how each of the energy system's contribute to to meet the physical demands of the sports.

Comments
Post a Comment