The Energy Systems' Response to Acute Exercise
What is ATP? ATP
is a
molecule that stores and releases chemical energy for use in body cells. ATP
stands for Adenosine triphosphate. It is a high energy compound. It is produced from glucose, and other energy sources when they are needed. those energy sources can be sored in the liver, muscles, or as fat tissue. The body transfers stored chemical energy to mechanical energy, and it does this by the breakdown of Adenosine and Triphosphate. This is ATP. It is released by the breaking down of the phosphates it releases energy for movement. Energy systems are used to break down ATP and then remote ATP to be broken down again. This process begins over and over again. The problem is that the muscles only store a small amount of energy compound (ATP) and it is limited to around 2 seconds wroth of energy. Energy systems are then used to remake the ATP for small bursts of energy, this is important for athletes like marathon runners as they are given small burst of energy and use them when they need to like to start and finish a race.
There are 3 systems which are used:
ATP-PCr it is formed and made up by ATP and creatine phosphate. T
his system is the immediate energy system. The creatine phosphate is a high- energy compound. Creatine phosphate is broken down to create energy to make ATP when exercise intensity is high or when the energy needs are instantaneous, it is stored in the muscles for when it has to be broken down.
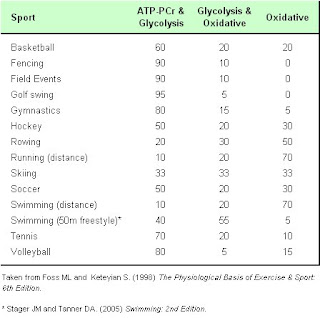
ADP+ creatine –ATP + creatine, this is the amount produced in the energy system.ATP is usually made without the presence of oxygen. Explosive work can be achieved, but only for up to about 10 seconds at maximum intensity, as the supply of PCr is limited. sporting examples include.
There are 3 systems which are used:
- Phospho- creatine system
- Lactic Acid System
- Aerobic System
ATP-PCr it is formed and made up by ATP and creatine phosphate. T
his system is the immediate energy system. The creatine phosphate is a high- energy compound. Creatine phosphate is broken down to create energy to make ATP when exercise intensity is high or when the energy needs are instantaneous, it is stored in the muscles for when it has to be broken down.
ADP+ creatine –ATP + creatine, this is the amount produced in the energy system.ATP is usually made without the presence of oxygen. Explosive work can be achieved, but only for up to about 10 seconds at maximum intensity, as the supply of PCr is limited. sporting examples include.
- Lifting the heaviest weight you possibly can for one or two repetitions. Personal training stopwatch
- Sprinting as fast as you can for 50 – 100 metres with 2-3 minute recovery intervals before repeating.
Lactic Acid System
This is also
known as the short term energy system. This is used to meet the requirements of
higher intensity over a longer period examples of this energy system would be:
- 400m race
- Track and field sprinting events
ATP can also
be formed from the breakdown of glucose and glycogen. Also sense this is a
anaerobic process it does not require oxygen and is therefore not suitable for
long duration sports like marathons and 10k runs. It may be sued at the start
and finish for the quick burst at the start and the burst at the end to finish
the race.There is
around 60-90 seconds of maximal work possible when using this system.
Lactic
acid is the limiting factor of the anaerobic systems. It accumulates and
diffuses into the tissue fluid and blood. If this substance builds up to impede
muscle contraction and cause fatigue. You may have experienced this as an
uncomfortable burning sensation in your muscles during intense exercise/
Aerobic Energy System
This is
known as the long term energy system. If plenty of oxygen is available, as it
is used during situations like: everyday movements and light exercise. Glycogen
and fatty acids break down to yield large amounts of ATP. This produces carbon
dioxide and water, which don’t affect the ability of muscles to contract. Aerobic
energy production occurs in the mitochondria of the cells. These are the power
stations of the cells, responsible for converting food into energy. The
production of energy within the aerobic system is slow to engage because it
takes a few minutes for the heart to deliver oxygenated blood to working
muscles. Long, continuous and moderate exercise produces energy using the
system. During
exercise the body does not switch from one system to the other- energy at any
time is derived from all 3 systems. However, the emphasis changes depending on
the intensity of the activity relative to the efficiency of your aerobic
fitness, i.e, the ability to deliver and utilise oxygen.
This is used
in sports such as
- Hockey
- Track and field distance events

Comments
Post a Comment